Please note that the official Node.js for Windows installer can now automatically install the required tools. That's likely a much better option than the module listed here (
windows-build-tools).
On Windows? Want to compile native Node modules? Install the build tools with this one-liner. Start PowerShell as Administrator and run:
npm install --global windows-build-tools
Or, if you are using Yarn:
yarn global add windows-build-tools
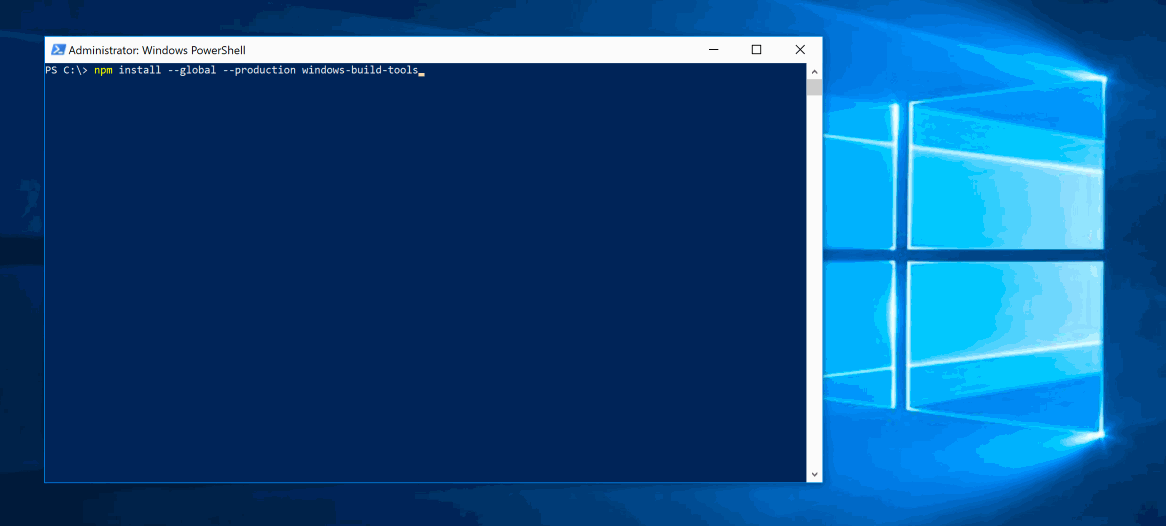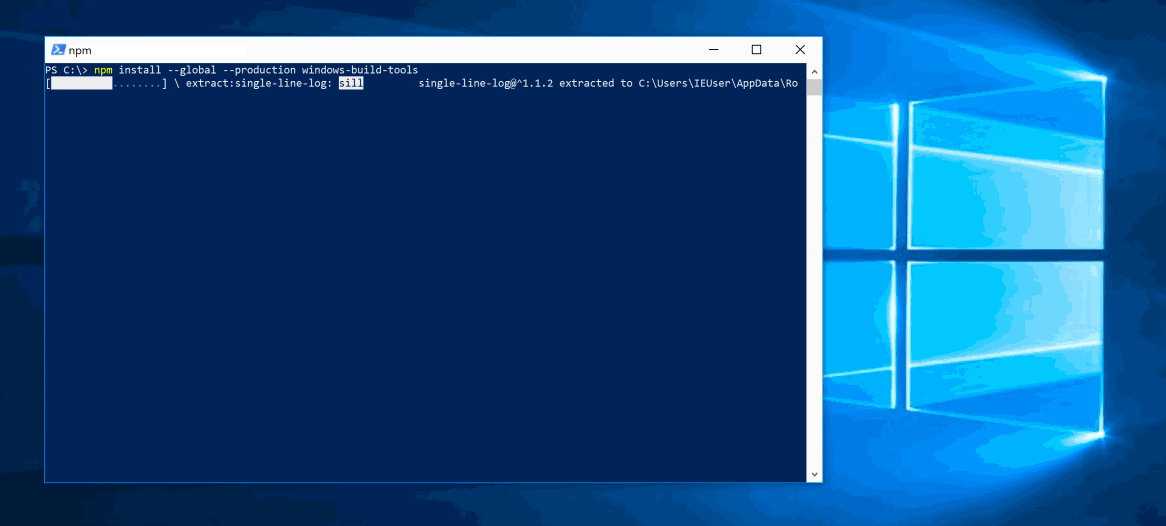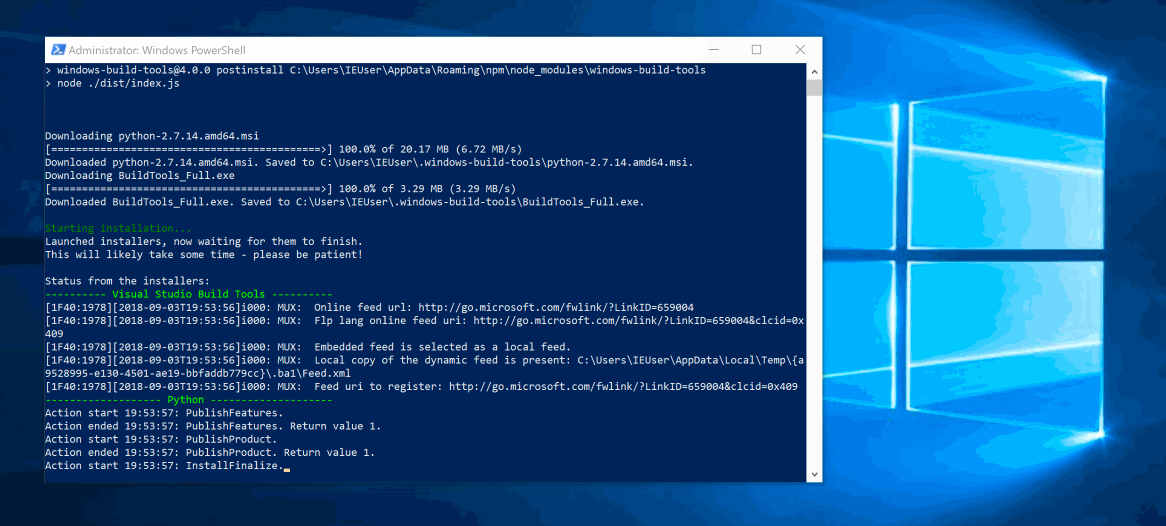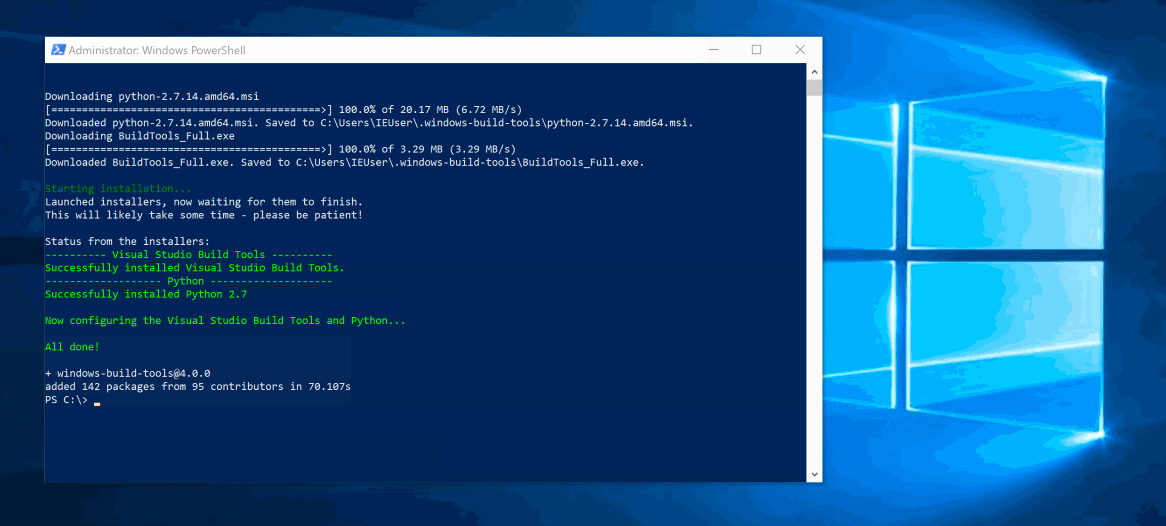
After installation, npm will automatically execute this module, which downloads and installs Visual C++ Build Tools, provided free of charge for most users by Microsoft (as part of Visual Studio Community, please consult the license to determine whether or not you're eligible). These tools are required to compile popular native modules. If not already installed, it will also install Python 3.8, configuring your machine and npm appropriately.
💡 [Windows Vista / 7 only] requires .NET Framework 4.5.1 (Currently not installed automatically by this package)
Both installations are conflict-free, meaning that they do not mess with existing installations of Visual Studio, C++ Build Tools, or Python. If you see anything that indicates otherwise, please file a bug.
This module is capable of installing either the build tools from Visual Studio 2017 or Visual Studio 2015.
By default, this tool will install the 2017 build tools. To change that, run this script with
the --vs2015 parameter.
npm [--python-mirror=''] [--proxy=''] [--debug] [--strict-ssl] [--resume] [--sockets=5] [--vcc-build-tools-parameters=''] [--vs2015] [--dry-run-only] install --global windows-build-tools
Optional arguments:
--offline-installers: Path to a folder with already downloaded installers. See--python-mirror: Use a given mirror to download Python (like--python_mirror=https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/python/). You can alternatively set aPYTHON_MIRRORenvironment variable.--proxy: Use a given proxy. You can alternatively set aPROXYenvironment variable.--debug: Be extra verbose in the logger output. Equal to setting the environment variableDEBUGto*.--strict-ssl: Enables "Strict SSL" mode. Defaults to false.--resume: By default,windows-build-toolswill resume aborted downloads. Set tofalseto disable.--sockets: Specifies the number of http sockets to use at once (this controls concurrency). Defaults to infinity.--vcc-build-tools-parameters: Specifies additional parameters for the Visual C++ Build Tools 2015. See below for more detailed usage instructions.--silent: The script will not output any information.--vs2015: Install the Visual Studio 2015 Build Tools instead of the Visual Studio 2017 ones.--dry-run-only: Don't actually do anything, just print what the script would have done.--include-arm64-tools: Include the optional Visual Studio components required to build binaries for ARM64 Windows. Only available with the 2017 and newer build tools and Node.js v12 and up.
You can pass additional parameters directly to the VCC Build Tools installer. This tool does not check if the parameters make sense - passing incorrect parameters might break the whole installation.
Supply parameters to windows-build-tools as a JSON array. Here's quick example (note the double quotes):
npm --vcc-build-tools-parameters='[""--allWorkloads""]' install --global windows-build-tools
If you run windows-build-tools with --vs2015, these parameters are available:
/AdminFile: Specifies the installation control file./CreateAdminFile: Specifies the location to create a control file that can then be used/CustomInstallPath: Set Custom install location./ForceRestart: Always restart the system after installation./Full: Install all product features./InstallSelectableItems: <item1;item2;...;itemN> Choose which selectable item(s) to be installed. -selectable item to be installed, just pass in this switch without any value./Layout: Create a copy of the media in specified folder./NoRefresh: Prevent setup checking for updates from the internet./NoRestart: Do not restart during or after installation./NoWeb: Prevent setup downloading from the internet./Passive: Display progress but do not wait for user input./ProductKey: <25-character product key> Set custom product key (no dashes)./PromptRestart: Prompt the user before restarting the system./Repair: Repair the product./Uninstall: Uninstall the product./Uninstall /Force: Uninstall the product and features shared with other products.
The available parameters are documented here.
By default, windows-build-tools will download the latest installers from Microsoft each time
it's installed. Alternatively, you can prepare a folder that contains installers. They need to
have their original names:
- Visual Studio Build Tools:
vs_BuildTools.exeorBuildTools_Full.exe - Python:
python-3.8.1.amd64.msiorpython-3.8.1.msi
Then, run windows-build-tools with the --offline-installers argument:
npm install -g windows-build-tools --offline-installers="C:\Users\John\installers"This package currently only handles the most common use case, none of the edge cases. If you encounter errors, we'd greatly appreciate error reports (and even pull requests). This is currently tested on Windows 10.
windows-build-tools4.0 and up require at least Node v8.windows-build-tools3.0 and up require at least Node v6.windows-build-tools1.0 and up require at least Node v4.
It's saved under %USERPROFILE%\.windows-build-tools\python38.
windows-build-tools works best if installed from an account with administrative rights. However,
thanks to @brucejo75, the following steps can be taken to install to a different user account:
- From your non-admin account (e.g. <Me>) run
cmd.exeas administrator. - Set the following environment variables in the new command shell:
set APPDATA=C:\Users\<Me>\AppData\Roaming
npm config set prefix C:\Users\<Me>\AppData\Roaming\npm
set USERNAME=<Me>
set USERPROFILE=C:\Users\<Me>
Ensure that the variables passed match your location of npm's roaming data and the location
of user profiles on your machine. For <me>, substitute the name of the account you want to
install windows-build-tools for. For more information, see the npm config set prefix
description here.
- Run
npm install -g windows-build-tools
In theory, windows-build-tools supports all pure C++ addons for Node.js (and virtually everything
else that requires a native compiler toolchain to be installed on your machine).
To ensure that that's true, we take a fresh Windows 10 installation, add windows-build-tools, and
ensure that the most popular native Node addons compile from source. Those are: node-sass, bcrypt, sqlite3, serialport, websocket, deasync, grpc, canvas, sharp,
hiredis, leveldown, nodegit, zqm, ffi, libxmljs, iconv, ref, sleep, microtime, couchbase, bignum,
kerberos, and ursa.
The Python installation was made possible by Ali Hajimirza, who kindly wrestled with Python's MSIs until they surrendered. For details regarding the license agreements applicable to Python, see History and License 3.x.
Use of Microsoft software is subject to the terms of the corresponding license agreements. For details regarding the license agreements applicable to Visual Studio products, refer to their License Directory page. (See also this discussion for the gist of it.)
Copyright (C) 2018 Felix Rieseberg. Licensed MIT. For more details, please see LICENSE. This license applies to this package only, not to its dependencies or the 3rd party software that it installs.